On Page SEO Learning in 7 Steps | Best Free SEO Tools


On Page SEO learn in 7 StepsIt’s time to dive into On page SEO, the art of crafting web pages that address the questions of searchers if you know how your target market is looking.
It is multifaceted and extends beyond content into other things, such as schema and meta tags On Page SEO, which in the next chapter on technical optimization we will address more in-depth. Put your wordsmithing hats on, for now, it’s time to produce your stuff!
Creating your content for On Page SEO
Applying your keyword research –
Here’s a simple outline for putting your keyword research into practice:
- Survey your keywords and group groups with similar topics and intentions. That group will be your pages, instead of creating individual pages for each keyword variation.
- If you haven’t already, evaluate the SERP for each keyword or group of keywords to determine what type and format your content should be. Some features of rating pages to note:
- Are they heavy-image or video?
- Is it long-form or short and succinct in content?
- Is the content in lists, bullets, or paragraphs formatted?
3. “Ask yourself, “What special value can I give to make my website better than the pages I currently rank for my keyword? ”
On Page SEO learn you to turn your research into content that your audience likes. Just make sure to avoid falling into the trap of low-cost tactics that can do more harm than good!
Low-value tactics to avoid in On Page SEO:
Your web content should be available to answer searchers’ questions, guide them through your site and help them understand the purpose of your site. For the purpose of ranking highly in search alone, content should not be produced.
The ranking in On Page SEO is a means to an end, and helping searchers is the end. We risk falling into the pit of low-value content strategies if we position the cart before the horse.
You may know some of these tactics but come to the review, dive deeper into some low-value tactics that you should avoid creating the search engine content you want.
Thin content in On Page SEO
While it is common for a website to have unique pages on a variety of topics, the older content strategy was to create a page for each repetition of your keywords so that the page for those highly specific questions Can be rated at 1.
For example, you could have produced individual pages for bridal gowns, bridal dresses, wedding gowns, and wedding dresses if you were selling bridal dresses, even if every page was basically saying the same thing. For local businesses, a common strategy was to build several pages of content for each city or area they needed customers from.
These “geo pages” often had the same or very similar content, and the only unique element was the location name.
Clearly, such a strategy was not useful to consumers, so why did publishers do it?
Google wasn’t always as good as it is today at understanding the relationships between words and phrases (or semantics) in On Page SEO learning. So, if you wanted to rate “bridal gowns” on page 1 but you only had a “wedding dresses” page, that would not have cut it.
The exercise spawned tons of thin, low-quality content across the web, which Google specifically addressed with its 2011 update, known as Panda.
This algorithm in On Page SEO update penalized low-quality pages, resulting in high-quality pages topping the SERPs. Google still repeats this process of demolishing low-quality content and promoting high-quality content.
Instead of several, weaker pages for each variation of a keyword, Google is clear that you should have a detailed page on a topic.
Duplicate content in On Page SEO
As it turns out, “duplicate content” refers to content that is shared between domains or between multiple pages in a single domain. “Scrapped” content goes one step further and uses articles from other sites and unauthorized content.
This may include taking the content and republishing it as it is, without adding any original content or value or modifying it slightly before republishing.
What is a canonical tag? A canonical tag (also known as “rel canonical”) informs search engines that a particular URL is the master copy of a page. The canonical tag avoids duplicate or “identical” content from displaying on various URLs, which might cause difficulties.
There are many valid reasons for internal or cross-domain duplicate content, so Google encourages the use of rail = canonical tags to point to the original version of web content. Although you just don’t need to know about this tag yet, the key thing to remember for now is that the word and value of your content should be exclusive.
Cloaking in On Page SEO learning:
A simple tenet of the rules for search engines is to show the same material to the crawlers of the engine as you would show to a human visitor. This means you can never conceal text in your website’s HTML code that can’t be seen by a regular visitor.
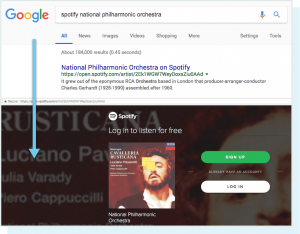
When this guideline is broken, search engines call it “cloaking” and take action to prevent these pages from being ranked in search results. Cloaking can be done, both positive and negative, in any number of ways and for a variety of reasons. An example of an instance in which Spotify showed users different content than Google is given below. (ON-PAGE SEO)
In Spotify, users were added to a login screen while searching for the National Philharmonic Orchestra 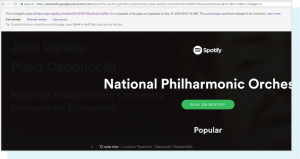
Viewing the cached version of Google’s website reveals the material that Spotify has supplied to the search engine.
In some cases, Google allows the passage of technically closed methods because they contribute to a positive user experience. For more information on the hidden content article and how Google handles it, see our Whiteboard Friday headline How Google Handles CSS + JavaScript “Hidden” Text?
Keyword stuffing in On Page SEO learning:
If you’ve ever been told, “You need to include critical keywords X times on this page,” you may have noticed confusion over the use of the keyword in action. Many people mistakenly think that if you only add a keyword to your page content once, you will automatically rank for it.
The fact is, while Google searches on the pages of your website for mentions of keywords and related terms, the page itself has to add value outside of sole use of keywords.
It won’t sound like it was written by a robot if a page is going to be useful to users, so integrate your keywords and phrases naturally in a way that is understandable to your readers.
Below is an example of a content-filled page that uses another old method: bolding out all your targeted keywords.
Auto-generated content in On Page SEO learning
The sort that is auto-generated or created programmatically with the purpose of manipulating search rankings and not supporting users is arguably one of the most offensive types of low-quality content.
By how little it makes sense to read, you can identify some auto-generated content; they are technically words in On Page SEO learning terms, but strung together by a machine rather than a human being.SEO)
It is worth noting that advances in machine learning have contributed to more sophisticated auto-generated content that will improve over time. Probably a factor as to why they’re doing so poorly.
In Google’s standard guidelines for self-generated content, Google specifically calls for a brand of auto-generated content that ranks higher in search rankings than any other auto-generated content, tries to manipulate.
What to do instead: 10x it! in On Page SEO
In search results, there is no “secret sauce” to rate. Google rates pages highly because they are the best answers to the questions of the searcher, it has decided. It’s not enough in today’s search engine that your page is not duplicated, spammed, or broken.
Your page searchers have to pay a price and Google is currently better than any other page that is currently offering an answer to a particular question. A simple formula for creating content in On Page SEO learning is:
- Check for the keyword(s) for which you want to rate your page
- Identify which pages are highly ranked by certain keywords
- Determine what attributes these pages have
- Build better content than that
This is 10x stuff, we like to call it. Google will award you for it if you create a page on a keyword that is 10x better than the pages seen in search results (for that keyword), and better yet, you will automatically get users linking to it! It’s hard work to produce 10x content, but it will pay dividends in organic traffic.
Just remember, there is no magic number when it comes to words on a page. What we should aim for is what satisfies the user’s intent to a great extent. Some questions can be answered completely and accurately in 300 words while others may require 1,000 words!
NAP: A note for local businesses in On Page SEO learning:
If you’re a company that makes in-person contact with your clients, be sure to prominently, correctly, and regularly include your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) throughout the content of your site.
This detail is also reflected in a local business website’s footer or header, as well as on any “contact us” pages. You may also want to use the local business schema to mark up this data.
If you’re a multi-location business, it’s best to create unique, better pages for each location. For example, businesses with locations in Seattle, Tacoma, and Bellevue should consider having one page for each:
example.com/seattleexample.com/tacomaexample.com/bellevue
In On Page SEO learning terms, each page should be enhanced by the unique uniqueness of this location, so the Seattle page will have unique content to discuss the Seattle location, the Seattle Knaps list, and even exclusively compliment Seattle users. ۔ If there are dozens, hundreds, or thousands of locations, you can use the Store Locator Widget to help you scale.
Local vs national vs international in On Page SEO:
“Just note that not all companies operate and conduct what we call “local SEO” at the local level. Some companies want to attract national customers (e.g., the entire United States) and others want to attract multi-country customers (“international SEO”).
For instance, take Moz. Our product (SEO software) is not connected to a particular spot, while a coffee shop is, so customers have to drive to the place to get their caffeine fix.
In this scenario, Coffee Shop should optimize its website for its physical location, while Moose will target “SEO software” without location variables such as “Seattle”.
How you want to customize your site depends primarily on your audience, so make sure that when designing your website content, you have them in mind.
Hope you still have some energy left after managing the difficult-yet-rewarding task of putting together a page that is 10x better than the pages of your competitors, because before your page is complete, there are just a few more items needed!
Best Free SEO Tools in On Page SEO learning:
There are hundreds of free SEO tools available, so you need to narrow it down to the best and most useful for you to add to your toolkit.
1. Bing Webmaster Tools
2. Data Studio
3. Enhanced Google Analytics Annotations
4. Google Analytics
5. Search Console
6. Keyword Hero
7. MozCast
8. Beam Us Up
9. Link Redirect Trace
10. Redirect Path
SEO Mozbar specifications? Is Mozbar Free?
MozBar is a free Chrome Extension that makes obtaining link data and performing SEO tasks on the move a breeze. MozBar shows link metrics for pages and domains while you search, such as Domain Authority, Page Authority, and the number of backlinks for each site.
You can employ all of MozBar’s advanced capabilities, including the keyword difficulty tool, page optimization, and advanced link metrics, if you pay for a paid Moz subscription. Simply visit the Chrome Web Store using Google Chrome and click “Add To Chrome” to add the MozBar Chrome Extension to your browser.
7 Legitimate Ways for On Page SEO learning:
- Know who you’re trying to reach.
- Understand the importance of keyword research and preparation.
- Build your website with keywords.
- Quality content will help you get authority and backlinks.
- Create, manage, and expand your social media presence.
- Learn how to use Google Analytics.
Learn SEO in 7 Steps:
- SEO Basic
- How Search Engines Work:
- Keyword Research
- On-Page SEO
- Technical SEO
- Link Building & Establishing Authority
- Measuring & Tracking SEO Success
Most Popular On Page SEO learning Blogs:
- Welcome to your SEO learning journey | Basic to Advance
- SEO-friendly blog post – 10 Tips for Writing
- Off-Page SEO: What It Is and Why It’s Important
- ON-PAGE SEO – Learn SEO in 7 steps | Basic to Advance
- What is a Search Engine? | Welcome to your SEO learning journey
- Keyword Research: How to Target and Prioritize keywords
- KEYWORD RESEARCH | Learn SEO in 7 Steps
- 7 Tips for keyword research in SEO – Things to Know
- WordPress SEO Tips | How to Boost Rankings
- Link building – How to build high-quality backlinks
- TRACKING SEO PERFORMANCE | Lean SEO in 7 steps