How to Use Serological Pipette Gun Holder 10ML
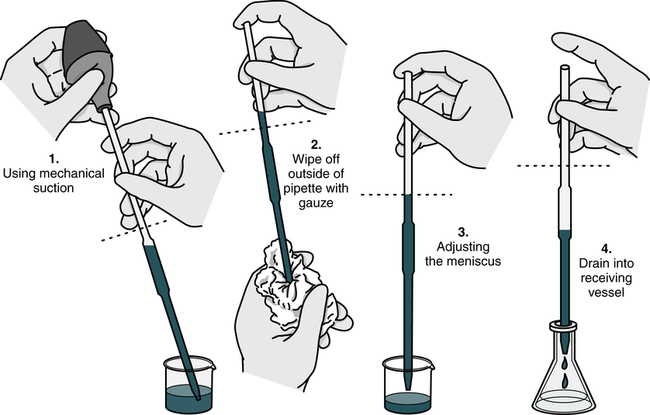
Serological pipettes are sterile tools that facilitate the precise dispensing of fluids while minimizing the risk of contamination. It is a laboratory instrument used for precise and accurate measurement and transfer of liquids. It is commonly used in scientific research, medical laboratories, and other analytical settings.
What is a Serological Pipette?
Serological pipettes are specifically designed for accurate and rapid fluid dispensing in laboratory settings. They are sterile, pyrogen-free, and cotton-plugged, making them suitable for a wide range of liquid handling applications. These pipettes are commonly used for transferring volumes ranging from a few milliliters to up to 100 mL using a serological pipettor. They are versatile tools that can be employed for mixing chemical solutions, cell suspensions, and transferring liquids with precise measurements. Serological pipettes are compatible with all serological pipettors, allowing for convenient and fast volumetric measurements. They facilitate the even distribution of cells, gentle mixing of suspensions and reagents, and gradient formation.
Sizes:
The serological pipettes are made from transparent polystyrene (PS) and are color-coded for convenient volume identification. They are offered in various sizes, including 1mL, 2mL, 5mL, 10mL, 25mL, and 50mL, to cater to different volume requirements.
Serological pipettes are offered in a range of sizes, from 1 mL to 50 mL, and are suitable for use with MACROMAN® or any pipette controller, manual pipette pump, or rubber bulb pipettes.
Color:
The serological pipettes have a patented color-coded wadding (yellow, green, blue, orange, and red) to facilitate easy recognition. They also have negative overgraduations for added convenience. These pipettes are available in case quantities ranging from 200 to 1,000 units.
3 Things You Should Know About Serological Pipettes
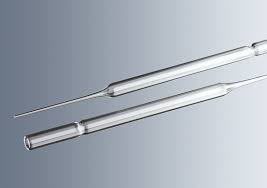
Pipette.com has compiled a guide outlining the key characteristics to consider when choosing a serological pipette.
1. The Design of a Serological Pipette
Serological pipettes are specifically designed for the precise and fast dispensing of fluids. They are made from sterile, medical-grade polystyrene to maintain a high level of cleanliness. These pipettes are pyrogen-free and are individually packaged to guarantee sterility, minimizing the risk of contamination.
2. Pipette Precision & Accuracy
In the past, serological pipettes were not known for their accuracy in measurements. However, modern serological pipettes have addressed this issue and now offer guaranteed accuracy and precision within a range of +1 to -2%.
To enhance both speed and accuracy in pipetting, you can consider using a Capp Motorized Pipette Controller, a Drummond Pipet-Aid, or explore a wide range of motorized pipette controllers. These devices assist in controlling the speed of aspiration and dispensing with improved precision.
3. Cost
It is important to consider the source of your purchase when buying serological pipettes. Choosing the right supplier can lead to significant cost savings. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the prices and compare them before making a purchase decision. Conducting a brief cost analysis can potentially save you a substantial amount of money.
How to read serological pipette
To read a serological pipette, hold it vertically and at eye level. The volume is indicated by the graduations marked on the pipette, typically in milliliters (ml). Read the volume by aligning the liquid level with the appropriate graduation line.
How to use a serological pipette.
In laboratory settings, serological pipettes are commonly employed for transferring liquid volumes ranging from less than 1 ml to up to 50 ml. These pipettes are available in two types: sterile, disposable plastic pipettes and sterilizable, reusable glass pipettes. Both types of pipettes are used in conjunction with a pipette, which aids in the aspiration and dispensation of liquids. The same pipet-aid can be used with different sizes of pipettes, allowing for versatility in various experimental assays.
Serological pipettes serve a variety of purposes, such as mixing chemical solutions or cell suspensions, transferring liquids between containers, and layering reagents with different densities. By carefully monitoring the liquid levels during aspiration and dispensation, serological pipettes prove to be valuable tools for accurately transferring milliliter volumes of solutions in laboratory settings. This video provides insights into reading volume measurements on serological pipettes, the functioning of a pipet-aid, and diverse applications of serological pipettes.
Primarily, the use of Serological pipette in the following:
- Mixing suspensions.
- Combining reagents and chemical solutions.
- Transferring cells for empirical analysis or expansion.
- Layering reagents for creating higher-density gradients.
Serological pipettes are a gentle and efficient method for mixing cell suspensions in laboratory settings. They are also suitable for blending reagents and chemical solutions. Following the treatment or isolation of experimental cell cultures, serological pipettes are valuable tools for transferring cell colonies to facilitate further empirical analysis or expansion.
Moreover, serological pipettes are utilized for the precise layering of reagents to create density gradients, such as ficolin gradients, which are employed in the purification of blood plasma cells.
To use a serological pipette, first select the desired volume by adjusting the volume control knob or dial on the pipette. Immerse the tip of the pipette in the liquid. Slowly and steadily press the plunger down to the first stop to draw in the liquid. Then, carefully transfer the liquid to the desired container by releasing the plunger gradually.
The use of a serological pipette is essential in various laboratory procedures, such as transferring liquids between containers, preparing samples, and conducting experiments. It ensures accurate and controlled dispensing of liquids, minimizes errors, and maintains the integrity of the experiment or analysis.
A serological pipette holder is a device used to hold serological pipettes upright, keeping them organized and within easy reach during laboratory work. It helps prevent contamination and damage to the pipettes.
The motorized pipet controller is a lightweight and ergonomic device specifically designed for use with glass and plastic serological pipets ranging from 0.5 mL to 100 mL in volume. It features conveniently positioned switches that allow for quick adjustments of operating modes and speeds to accommodate different liquid volumes and viscosities.
A serological pipette gun is a mechanical device used to aspirate and dispense liquids using serological pipettes. It provides a convenient and ergonomic alternative to manual pipetting, allowing for precise and controlled liquid transfer.
A pipette gun or controller, also referred to as a pipette aid or pipettor, is a laboratory instrument employed for precise aspiration and dispensation of small liquid volumes. It is extensively utilized in scientific and medical fields, such as molecular biology, biochemistry, cell culture, and clinical diagnostics, to perform a wide range of applications.
10 ml serological pipette can be used to accurately measure and transfer 10 milliliters of liquid in laboratory experiments, sample preparations, or analytical procedures. It provides a reliable method for dispensing a specific volume of liquid with precision. It is suitable for various applications, such as mixing solutions, transferring samples, and layering reagents.
Are serological pipettes sterile?
Serological pipettes are glass or plastic pipettes with graduated markings that are utilized for the precise measurement and dispensing of specific liquid volumes. They can be classified as either Class A or Class B based on their tolerances. Additionally, they may be labeled “to “To Contain” or “to deliver,” depending on their intended use. Serological pipettes can be obtained in sterile or nonsterile forms.
Volumetric pipette vs Serological pipette
Serological pipettes are versatile tools that feature multiple graduations and are commonly employed for general liquid transfer purposes. On the other hand, volumetric pipettes are highly precise instruments specifically designed for measuring specific volumes with a high degree of accuracy. Volumetric pipettes are typically used in applications that require precise and accurate measurements.
Let’s wrap it up:

Serologic testing is an essential component of diagnostic tests in clinical laboratories for viral and bacterial diseases. It is widely used in various areas of the clinical laboratory, such as microbiology, chemistry, toxicology, immunology, hematology, surgical pathology, cytopathology, and immunohematology (blood banking). Serologic and immunologic tests can be performed on a wide range of specimens. Both rapid testing in the laboratory and home-testing kits are commonly used.
The development of monoclonal antibody (MAb) technology has greatly enhanced the specificity and sensitivity of immunoassays. Some common serologic and immunologic tests include pregnancy tests for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and tests for infectious mononucleosis and syphilis.
The serologic pipette resembles a graduated pipette but has a larger orifice or tip opening. However, due to the fast rate of liquid flow, it is not ideal for high accuracy or precision measurements.
The serologic pipette can be identified by a frosted ring at the non-calibrated end, with calibrations extending to the tip. It is marked with the letters “TD” (to deliver) and has a color-coded band indicating the volume for quick recognition. Emptying the serologic pipette is usually done by gravity, and depending on the calibration, the remaining drop may need to be expelled to deliver the full volume.
Each serologic pipette is labeled with identifying numerals, such as 10 mL, indicating the total capacity of the pipette. The second number represents the smallest division or gradation of the pipette. For example, a pipette marked as 10 mL is divided into 1 mL sections, and each milliliter is further divided into tenths. Commonly used sizes of serologic pipettes include 10 mL, 5 mL, 2 mL, and 1 mL. Using the smallest pipette that can hold the desired volume ensures the highest accuracy.
Read More: