What is Ecommerce Warehouse Management System: Best Practice

As an ecommerce merchant, effective ecommerce warehouse management is crucial for a smooth supply chain, cost and time savings, and customer satisfaction. As your business grows, ecommerce warehousing becomes more complex, requiring the implementation of best practices to optimize your supply chain, whether through in-house management or working with third-party logistics companies (3PLs).
Due to the increasing demand for warehousing, the industry has responded by constructing more storage space. By the end of 2021, a record-breaking 520 million square feet of warehouse space was under development, representing a 50% increase from the previous year.
This article will explore the current state of eCommerce warehousing and help you determine the most suitable ecommerce warehouse solution for your business.
What is Ecommerce Warehousing?

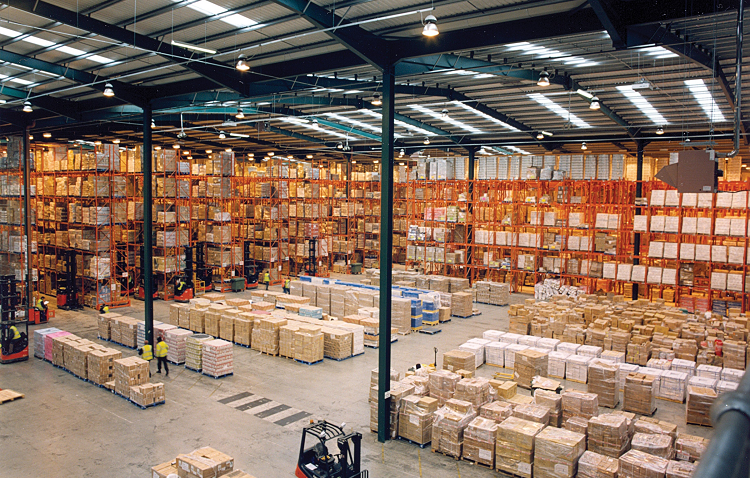
Ecommerce warehousing involves the storage of physical goods before their sale online. It encompasses the secure and organized storage of products, as well as the tracking of inventory, including arrival dates, stock duration, and available quantities at any given time.
In many cases, a third-party logistics provider (3PL) incorporates a warehouse as a vital component of their ecommerce warehouse fulfillment operations. Through a sophisticated network of systems, the 3PL strategically organizes products within the warehouse to ensure efficient picking and packing processes when online orders are received. The 3PL also handles the reception of products from manufacturers and collaborates with shipping carriers to arrange product pickups for onward delivery to end-customers or retailers. A reliable warehouse typically utilizes a comprehensive set of operations, including an IT warehouse management system and human operators who assist with product packaging and other tasks.
The most common ecommerce warehousing operations include:
- Implementing safety and security measures for inventory storage
- Receiving and storing inventory in the ecommerce warehouse
- Organizing and optimizing bin, shelf, and/or pallet locations for each SKU
- Conducting regular warehouse audits and inventory audits
- Maintaining accurate records of stock levels and generating inventory reports
To streamline their operations, many ecommerce warehouse managers opt for specialized ecommerce warehousing and ecommerce warehouse management systems. This guide will provide an overview of ecommerce warehouse and ecommerce warehouse management, including the different types of ecommerce warehouse. Additionally, it will explore the benefits of using an ecommerce warehouse management system compared to a traditional warehouse management system.
Why is ecommerce warehousing important?
During different growth stages, an ecommerce business may encounter the following situations:
- Outgrowing the initial storage space.
- Needing an overflow location for excess safety stock.
- Deciding to purchase land or lease an additional warehouse.
- Investing in fulfillment infrastructure, including staff, technology, certifications, shipping supplies, forklifts, conveyors, and other equipment.
- Requiring multichannel inventory management capabilities to accommodate new sales channels.
- Opening or expanding into a second fulfillment center to reduce transit times and shipping costs.
- Scaling up international fulfillment capabilities to establish a global brand.
How Does Warehousing Fit into Ecommerce Fulfillment
A ecommerce warehouse typically focuses on storage and is used for longer-term storage of products over months or years. Its primary function is to provide space for storing goods.
On the other hand, a fulfillment center is a more dynamic type of warehouse. While it may have areas dedicated to long-term storage, it also includes sections for various operational activities such as picking, packing, kitting and assembly, labeling, sorting, and specialized areas like refrigeration or controlled environments for specific products.
The primary role of a fulfillment center is to offer dedicated space to ecommerce companies for receiving, processing, sorting, and shipping goods to end customers who have made online purchases. A fulfillment center can be owned and operated by a single company or managed by a third-party logistics provider (3PL) or fourth-party logistics provider (4PL) to handle products from multiple companies.
Inventory Management
Proper organization and accurate inventory management are crucial within a ecommerce warehouse to maintain the optimal number of SKUs. The goal is to fulfill orders promptly while avoiding excess inventory that would turn the distribution center into a storage warehouse. This entails accurate forecasting of order volume, effective communication with manufacturers and freight forwarders for regular product deliveries, and employing a reliable inventory management tool to monitor real-time stock levels.
By implementing these measures, businesses can prevent stockouts and minimize delays in customer shipments caused by backorders. If inventory is stored across multiple warehouses, it’s essential to understand the resources, planning, and tools required for a successful distributed inventory strategy.
A well-equipped warehouse will feature systems that provide accurate and up-to-date inventory counts at any given time, enabling efficient inventory management and order fulfillment.
Order Picking
When an end-customer submits an online order, the distribution center is notified to initiate the picking process from the warehouse shelves. Picking, which involves selecting the correct items for each order, is a labor-intensive aspect of the supply chain. In large warehouses housing multiple SKUs for various companies, efficiently locating the right item is a significant undertaking. Modern fulfillment center warehouses employ robust systems to ensure accurate and efficient picking. Various picking methods are utilized, including single-order picking, batch picking, zone picking, and others, depending on the specific requirements and operational setup of the ecommerce warehouse.
Kitting & Assembly
After picking, the order moves to a station within the distribution center for packing into a shipping container. Additional materials or items may be included before the order is packaged, labeled, and prepared for shipment.
Certain basic third-party logistics providers (3PLs) offer only picking and packing services. In such cases, individual items or orders are picked and directly placed into a parcel, labeled, and shipped. However, 3PLs offering value-added services and customizable fulfillment solutions go the extra mile to ensure their clients can provide the exact experience desired by end customers.
Assembly involves gathering multiple components and assembling them into a single item. For consumer electronics products, this might involve assembling a few parts before packaging or even updating software to the latest version. Kitting, on the other hand, involves adding multiple items to the same order.
Accurate kitting and assembly require modern IT infrastructure within the distribution center ecommerce warehouse to ensure that the correct items and components are placed in the appropriate packages, maintaining efficiency and order accuracy.
Shipping & Receiving
Fulfillment center warehouses typically have multiple carrier pickups throughout the day. The choice of carrier service depends on the quantity of products being picked up and their destination. The warehouse must have designated docks and stations configured to handle different volumes of goods. For instance, if multiple pallets of goods are being shipped to a retailer, the dock should be able to accommodate large freight carrier trucks. For direct-to-consumer (DTC) pickups, smaller box trucks and carrier vans are required for handling smaller quantities of products.
The ecommerce warehouse’s role in shipping and receiving is to optimize a smooth transition of activities at each loading dock. The warehouse needs to have an updated system for scheduling dock bookings. Otherwise, there is a risk of trucks and carriers competing for time, leading to congestion, waiting times, and frustration. Efficient dock management is vital to ensure a streamlined flow of goods in and out of the warehouse.
Returns Management
Returns management, or the process of handling returned items, is a significant aspect of any ecommerce warehouse business, although some smaller companies tend to overlook it. A warehouse should have a streamlined system in place to efficiently receive and process returned items, regardless of the reason for return.
Certain warehouses and third-party logistics providers (3PLs) go the extra mile by offering additional services such as refurbishment of returned products, disposal of returned items, and even real-time tracking for end-customers to ensure smooth returns management and customer satisfaction. These added steps can enhance the overall returns experience for both the business and its customers.
Why Many Ecommerce Warehouses Are Garages or Living Rooms
Many ecommerce businesses start small and operate out of garages or living rooms as warehouses due to their low cost and convenience, especially in the early stages of growth.
1. Business operates from home.
Operating an ecommerce business out of garages or living rooms as makeshift warehouses allows business owners to closely monitor their inventory, efficiently pack and ship orders from the comfort of their homes, and conveniently receive new inventory directly at their doorstep.
2. Warehousing costs too much.
Acquiring warehouse space through leasing or purchasing can be costly, especially for e-commerce businesses that sell a diverse range of products and require larger storage space.
3. Owners feel they’re too small to outsource.
If a business is unable to afford or acquire its ecommerce warehouse, there are alternatives to utilizing personal spaces like garages or living rooms. One option is to utilize third-party warehousing services.
4 Benefits of Warehousing Your Ecommerce Products
Utilizing external ecommerce warehousing can offer significant advantages to businesses. Here are four benefits of using external warehousing for your inventory:
1. Easier to stay organized
By using an external ecommerce warehouse, businesses can benefit from increased space and improved organizational systems. This facilitates easier management of inventory tracking and customer orders. Engaging a third-party logistics (3PL) provider can relieve businesses of the tedious task of inventory management and provide efficient product monitoring services.
2. More accurate picking and packing
3PL services extend beyond ecommerce warehousing to encompass warehouse picking and packing, alleviating a significant portion of the fulfillment process. 3PL providers employ specialized staff for various aspects of order fulfillment and supply chain optimization. Their advanced technology and streamlined processes help guarantee accurate packaging and timely delivery of the right products, contributing to a positive customer experience.
3. Time to focus on growth
Using a 3PL provider for ecommerce warehousing allows businesses to focus their time, attention, and resources on critical growth-related activities. By entrusting warehousing tasks to the 3PL, businesses can allocate their resources to functions like customer expansion. In this way, the ecommerce warehouse becomes a contributing factor to the overall growth and success of the business.
4. Ship to your customers faster.
When deciding on inventory storage, it is beneficial to distribute it across multiple warehouses nationwide. This strategy positions the inventory closer to a larger customer base, resulting in reduced delivery times and costs for online orders, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
5. Less stress and Time Savings.
Ecommerce warehousing encompasses much more than simply storing products on shelves. Entrusting the multitude of warehousing responsibilities to a capable provider can bring immense relief. A well-organized process and the assurance that your products are being handled effectively can make a significant difference.
For ecommerce merchants, time is a valuable resource. By eliminating the need to search through piles of products or engage in storage Tetris, you can redirect your focus toward business growth. Often, the time savings achieved by outsourcing warehousing can offset the associated costs, as time is a valuable asset in the business world.
Types of e-commerce warehouses
Ecommerce warehouses encompass various types of warehouses that can meet the storage needs of an ecommerce business. While it is ideal to store ecommerce inventory in a dedicated ecommerce warehouse for optimal efficiency, there are different types available to choose from. It’s important to note that not all of them require a substantial investment, allowing businesses to select a type that suits their specific requirements and budgetary constraints.
1. Public warehouses
Public warehouses, typically owned by government agencies and rented out to businesses, offer affordable storage options with controlled rates and amenities. While they may be smaller and less advanced compared to private warehouses, they can still meet the storage needs of ecommerce startups and companies with limited budgets. Public warehouses are suitable for short-term storage requirements and can serve as a viable option during the initial stages of growing an online store. Although they may have limitations, they provide a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to manage their inventory without significant financial investment.
2. Private warehouses
Private warehouses are owned or rented by specific businesses and are designed to meet their specific needs. They are typically more expensive to purchase or rent compared to public warehouses. Private warehouses offer advantages such as customized sizes, updated warehouse management systems, and specialized construction for storing specific products (e.g., seafood storage with freezers near the sea). These warehouses are suitable for e-commerce SMBs, private distributors, and wholesalers due to the long-term benefits they provide.
An example of a company with private warehouses is Amazon, which owns a significant amount of fulfillment and data center space. Private warehouses are often more technologically advanced, with larger floor areas and tailored features like temperature control or specialized storage facilities.
However, it’s important to note that private ecommerce warehouses require significant capital investment and are primarily utilized by businesses with substantial financial resources.
3. Government-owned warehouses
Government-owned warehouses often offer high levels of security, making them a reliable option for storing valuable e-commerce products. These warehouses typically provide affordable rates for businesses. However, it’s important to note that if a business is unable to pay the rent for the warehouse, the government may exercise its right to sell the stored goods to recover its financial losses.
4. Consolidated warehouses
Consolidated warehouses play a crucial role in collecting shipments from various suppliers and grouping them into larger shipments for distribution to buyers. This process helps businesses reduce the costs associated with e-commerce transit, making it an attractive option for startups and businesses in their early stages.
One advantage of utilizing consolidated warehouses is the ability to maintain a low inventory threshold. With inventory from multiple sellers stored together, there is no need to keep a large volume of goods at the ecommerce warehouse.
However, it’s important to note that this mode of shipment is effective only when all goods are intended for the same geographical location or city.
Consolidated warehouses offer cost-effective solutions for ecommerce startups and businesses, making them an ideal choice for those seeking affordability and streamlined logistics operations.
5. Cooperative warehouses
Cooperative warehouses function similarly to private warehouses but have multiple owners who share the facility and resources. These warehouses can be utilized by members engaged in different lines of work but collaborate on a shared project. By sharing the costs of running the warehouse, each member only pays a portion of the fees involved. Cooperative warehouses offer a cost-effective warehousing solution for businesses in partnership, allowing them to pool resources and benefit from shared expenses.
6. Bonded warehouses
Bonded warehouses can be either privately or government-owned and are typically located near ports or airports. They serve the purpose of storing imported dutiable items, known as “bonded goods,” until customs taxes and duties are paid.
When a business rents a bonded warehouse, customs authorities issue a “bond” as government-certified proof that the space is being used to store goods. This bond helps businesses avoid financial losses, such as fines, for not immediately paying customs duties. Bonded warehouses are particularly beneficial for ecommerce businesses engaged in international sales.
Importing businesses often utilize bonded warehouses to improve cash flow and achieve cost savings. Customs duties are only paid when goods are sold and leave the warehouse, rather than immediately upon entering the borders. This allows sellers to allocate additional resources to pre-sale activities such as advertising and legal work, enhancing their overall business operations.
7. Smart warehouses
Smart ecommerce warehouses are at the forefront of e-commerce automation, utilizing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize workflow and improve operational efficiency. Amazon’s fulfillment centers serve as a prime example of smart warehouses, where automation technologies like conveyor belts, scanning technology, picking robots, drones, AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems), automated vehicles and carts, and robotic arms are employed to replace manual labor.
Unlike other types of warehouses, smart warehouses go beyond software automation and incorporate a range of advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and productivity. While these warehouses offer significant advantages in terms of automation and streamlined operations, they also come with a high price tag. Amazon’s fulfillment centers are well-known examples of smart warehouses in the e-commerce industry.
Ecommerce warehousing best practices
Proper warehouse management adheres to best practices in ecommerce warehousing to enhance profitability and deliver a superior customer experience.
Use a warehouse management system (WMS)
A warehouse management system (WMS) is specialized software that provides key features to optimize ecommerce warehouses. A WMS can:
- Track inventory in real-time
- Manage order fulfillment and picking processes
- Optimize warehouse layout and storage locations
- Automate inventory replenishment
- Generate reports and analytics for data-driven decision-making
- Integrate with other systems such as e-commerce platforms and transportation management systems
- Improve accuracy and efficiency through barcode scanning and automation
- Enable better visibility and traceability of products within the warehouse
- Facilitate labor management and task allocation
- Enhance overall operational efficiency and productivity in the warehouse.
Integrate your ecommerce store (and other tools)
Integration with your ecommerce store allows for seamless inventory management. Warehouse management software enables real-time stock availability tracking, simplified inventory forecasting, and the ability to set reorder points in advance to prevent shortages.
Distribute your inventory
Distributing inventory across multiple warehouses can help reduce shipping costs by automatically preparing and dispatching orders from the nearest distribution center to the customer. This strategy improves the customer experience with faster and more cost-efficient delivery.
Test multiple picking systems to find the right one
E-commerce businesses have various picking systems to choose from. Small organizations that handle a few orders per day may prefer the “one-order-at-a-time” picking process. However, for larger e-commerce businesses, more advanced tools are available. These tools facilitate batch picking and automatically generate picking lists based on the proximity of ordered items in the warehouse. This approach reduces walking paths and minimizes the time required to pick an order, improving efficiency and productivity in the ecommerce warehouse.
Set inventory minimum points
Achieving the right inventory balance poses a challenge for businesses. Ordering excessive products can harm profits and result in high carrying costs, while insufficient inventory can lead to out-of-stock situations and customer dissatisfaction. To address this, setting mandatory inventory minimums is a prudent measure. Quality software enables businesses to establish reorder points, triggering notifications when products reach specific thresholds. This allows for timely replenishment, ensuring optimal inventory levels and minimizing the risk of stockouts or excessive carrying costs.
How can ecommerce warehouse management systems help you?
An ecommerce warehouse management system is specifically tailored to handle the unique requirements of an ecommerce warehouse. It offers several advantages over a traditional system, including:
- Integration with e-commerce platforms for seamless order processing and inventory management.
- Real-time inventory visibility to prevent overselling and stockouts.
- Automation of order fulfillment processes to improve efficiency and speed.
- Advanced picking and packing features to optimize order accuracy and reduce errors.
- Integration with shipping carriers for streamlined shipping and tracking.
- Enhanced reporting and analytics capabilities for better decision-making in e-commerce operations.
Designed for single-item orders
Traditional warehouse management systems are designed for warehouses that handle orders with multiple items, typically using pallets, racks, and other large equipment. In contrast, ecommerce operations primarily involve single-item orders. According to Peoplevox, approximately 80% of orders received by ecommerce businesses consist of just one product. This unique characteristic of ecommerce necessitates specialized warehouse management systems that can efficiently handle the high volume of individual orders and the associated picking and fulfillment processes.
Able to withstand demand fluctuations
Warehouses experience fluctuations in consumer demand due to changing trends and seasonal variations. To effectively manage these fluctuations, a system is needed to handle incoming orders, along with a robust server capable of handling website traffic from customers. An ecommerce warehouse management system (WMS) can provide the necessary features to manage orders and ensure the website can handle the increased traffic during peak demand periods, facilitating smooth operations and customer satisfaction.
Accurate inventory management
Accurate inventory management is crucial for showcasing real-time stock availability to customers, creating a sense of urgency to purchase before items run out of stock, as seen on platforms like Amazon. An ecommerce warehouse management system (WMS) enables precise tracking of incoming and outgoing inventory. By integrating with the ecommerce platform, the WMS ensures seamless synchronization, allowing for efficient inventory management and a smooth customer experience.
Handling more returns
Indeed, the return process in ecommerce involves several essential steps that must be executed accurately to ensure a seamless and efficient process. From the buyer initiating the return to updating inventory, and order status, and notifying the customer, each step plays a crucial role in successfully processing the return. Any errors or delays in these processes can disrupt the flow and impact customer satisfaction.
Ecommerce businesses have specific requirements and unique processes compared to traditional warehouses. Utilizing a dedicated ecommerce warehouse and an appropriate ecommerce warehouse management system can significantly improve operational efficiency. Such systems are designed to handle frequent changes in demand, cater to single-item orders, manage high return volumes, and enhance overall performance in the dynamic ecommerce environment. By streamlining operations and automating key processes, businesses can better meet customer expectations and optimize their ecommerce operations.
Where is DHL ECOMMERCE WAREHOUSE located?
DHL is a leading global player in 3PL logistics and offers partnership opportunities to develop your omnichannel strategy, rapidly scale your operations, and optimize execution while maintaining control over your end-to-end customer experience.
By collaborating with DHL, you gain access to their unmatched e-commerce expertise, industry-leading fulfillment capabilities, and extensive last-mile network worldwide.
DHL eCommerce Warehouse is located at 191 Blair Rd Avenel, NJ, 07001-2026, United States.
Ecommerce Warehouse Management System: Best Practice
See Also:
- 6 Basics of How to Scale Your Ecommerce Business the Right Way
- What are the Risks of Selling Electronic D2C Products: D2C Ecommerce
- 5 Best Tips to Choose Ecommerce Business Name Ideas
- What is Ecommerce Business Intelligence: 5 Top Tools for BI
- Print-on-Demand Shoes Ecommerce Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- eCommerce Affiliate Network | 10 Affiliate Platform
- Wix eCommerce vs Shopify | 8 Top Ecommerce Platforms
- 6 Best Funding for Ecommerce Business Loans
- What are the Risks of Selling Electronic D2C Products: D2C Ecommerce
- B2C vs D2C Marketing: Which One Right for You: Best Examples
- Best Shopify Product API: Create Shopify API and Boost %100 Your Products
- 7 Best eCommerce Integration Platform: Benefits CRM ERP
- Ecommerce Warehouse Management System: 5 Best Practice Setup