What is Cloud Computing with Example | Type of Cloud Computing

On-demand access, often known as cloud computing, refers to the supply of various services over the Internet, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. Instead of being stored on your computer or other local storage, these off-site solutions are hosted in the cloud (or on the internet).
The term “cloud” simply refers to the internet. Computing refers to the infrastructure and mechanisms that enable a computer to run, produce, deploy, and interact with data. This means that instead of hosting infrastructure, systems, or apps on your hard drive or on an on-site server, you host them in the cloud.
Table of Content:
- Who Owns the Cloud?
- Why do we need to move to the Cloud?
- How does the Cloud work?
- Types of cloud computing
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Serverless computing
- Uses of cloud computing
Who Owns the Cloud?
Cloud computing, in its most basic form, entails storing and accessing data and programs over the internet rather than on your computer’s hard drive.
The cloud is essentially a series of servers, storage, databases, networking, applications, analytics, and intelligence that are located in vast, acre-filling complexes and operated by some of the world’s largest companies.
Companies with fluctuating or rising bandwidth requirements can use cloud-based platforms. If your needs grow, you can easily expand your cloud resources by using the service’s remote servers.
Why do we need to move to the Cloud?
Cloud computing is becoming increasingly common among mid-size and small businesses, allowing them to access application software over a high-speed internet connection without having to invest in computer software or hardware.
Data backup and recovery are simplified when you move to the cloud. Since your company data and resources are stored in the cloud, you’ll still have access to them, even if your desktop, smartphone, or tablet breaks down.
Cloud storage provides a range of data security and recovery options.
How does the Cloud work?
A consumer connects to at least one data server via the internet to use cloud storage.
The user sends files to the data server via the Internet, either manually or automatically, and the information is forwarded to multiple servers.
The information is then accessed through a web-based browser.
Information is housed in data centers all over the world and is managed by a third party in cloud computing. Since the data is stored on hosted servers, it can be accessed through a web interface.
A chain of servers is used for cloud storage and involves both a master control server and other storage servers.
Types of cloud computing:
A variety of models, sizes, and services have emerged to help you find the best solution for your needs. So first, you need to determine the type of cloud deployment, or cloud computing architecture, that your cloud services will be implemented on.
There are three methods for deploying cloud services:
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
Public cloud:
The cloud provider owns and manages all hardware, applications, and other supporting resources in a public cloud. A web browser is used to access these resources and maintains your account.
Public clouds, which distribute computing resources such as servers and storage over the Internet, are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers. Cloud computing that is distributed across the internet and spread across organizations is known as public cloud computing.
Many enterprise companies are turning to the public cloud as a way to scale existing IT resources on-demand without having to invest in new physical infrastructure. For instance, instead of purchasing a physical desktop computer, a company may purchase a virtual desktop license.
Private cloud:
A private cloud (also known as internal cloud or corporate cloud) is a type of cloud environment in which cloud software is handled by internal IT. Internal activities, for example, install and manage the Cloud Management Platform (CMP) for private IaaS infrastructure. Simply put, a private cloud is one in which services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network.
What is private vs public cloud?
Cloud computing that is distributed over the internet and shared by various organizations is known as public cloud computing. Private cloud is cloud computing that is entirely dedicated to your organization.
Hybrid cloud:
Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds, binding technology together to share data and applications. for example, with orchestration between the various platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
Hybrid cloud services are powerful because they give businesses maximum control over their private data
SEGA, one of the world’s leading video game companies, is using a hybrid cloud to provide flexible and agile production and testing environments for their global workforce of developers.
IaaS, PaaS, serverless, and SaaS are examples of cloud services.
The four major categories of cloud computing services are infrastructure as a service (IaaS), application as a service (PaaS), serverless computing, and software as a service (SaaS).
You have various degrees of power, versatility, and management depending on the cloud service and implementation system you use. They are sometimes called cloud computing “stacks” because they are built on top of each other.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS):
IaaS the most basic building block of cloud computing services, which provides high-level APIs that can be used to dereference various low-level information of underlying network infrastructure such as physical computing resources, location, data partitioning, scaling, protection, backup, and so on.
You rent IT infrastructure—servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, and operating systems—on a pay-as-you-go basis from a cloud provider with IaaS.
Platform as a service (PaaS):
Platform as a service refers to cloud computing services where a third-party provider delivers hardware and software tools to users over the internet.
PaaS was created to make it easier for developers to create web or mobile apps without worrying about the infrastructure or maintaining the underlying infrastructure of servers, storage, network, and databases.
Serverless computing:
Serverless computing is a cloud computing execution model in which the cloud provider allocates computer resources on-demand and operates the server on the users’ behalf.
You can focus on only writing code that serves your customers with serverless computing, infrastructure management tasks like capacity provisioning and patching are handled.
The cloud provider is in charge of setup, storage planning, and server management. Serverless architectures are scalable and event-based, using resources only when a particular action or stimulus is generated.
Software as a service (SaaS):
Software as a service (SaaS) is a method of distributing software applications over the Internet on demand and usually by subscription.
SaaS allows cloud providers to host and maintain software applications and underlying infrastructure, as well as handle maintenance such as software updates and security patching. Users access the app through the Internet, typically via a web browser on their phone, tablet, or computer.
Uses of cloud computing:
Even if you don’t know it, you’re probably using cloud computing right now. Cloud storage is almost definitely at the heart of it, If you use an online service to send an email, edit documents, watch movies or TV, listen to music, play games, or store images and other files.
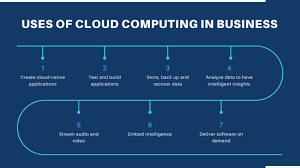
Top 7 Most Common Uses of Cloud Computing:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Hybrid cloud and multi-cloud.
- Test and development.
- Big data analytics.
- Cloud storage.
- Disaster recovery.
- Data backup.
Here are a few examples of what cloud services from a cloud provider can do today:
Develop applications that are cloud-native:
Build, deploy, and scale web, mobile, and API applications easily. Containers, Kubernetes, microservices architecture, API-driven communication, and DevOps are examples of cloud-native technologies and approaches.
Software development and testing:
Use cloud infrastructures that can quickly be scaled up or down to reduce application development costs and time.
Data storage, backup, and recovery:
Transferring your data over the Internet to an offsite cloud storage system that’s available from every location and device is a more cost-effective way to secure your data on a wide scale.
Analyze data:
Integrate your data across teams, divisions, and locations in the cloud. Then, using cloud services like machine learning and artificial intelligence, you will discover knowledge that will help you make better decisions.
Audio and video can be streamed:
With high-definition video and audio that is distributed globally, you can connect with your audience anywhere, at any time, on any device.
Integrate intelligence:
Using intelligent models to help consumers interact and gain useful insights from the data collected.
On-demand app distribution:
On-demand applications, also known as software as a service (SaaS), allow you to provide customers with the most updated software versions and updates at any time and from any place.
Cloud computing and Microsoft:
Microsoft is a leading provider of cloud computing services for organizations of all sizes around the world. To learn more about the Microsoft cloud platform, like Kubernetes on Azure offering, our serverless application platform, and how Microsoft Azure matches up against other cloud providers, visit the Microsoft Azure website.